Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!
Blog
-
Emotional healing Compare mental health landscape
Emotional Dissonance vs Healing
When internal emotions conflict with external performance,
psychological strain silently accumulates.📖 Prefer a detailed explanation? Read the full psychology article here.
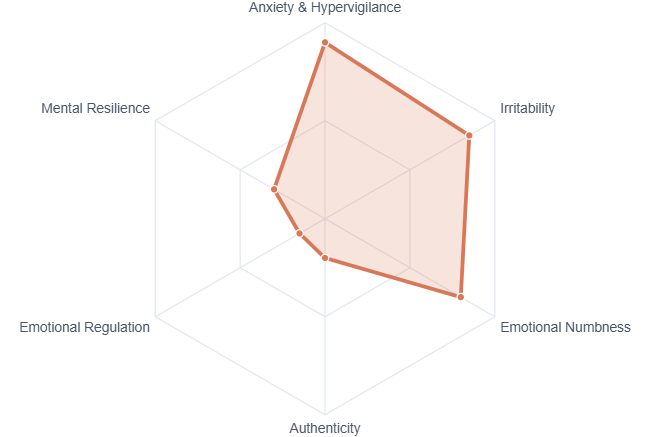
High anxiety, emotional masking, internal conflict.
Psychological health is not achieved by suppression
Healing occurs through awareness, regulation, and integration —
not avoidance.Zohaib Ali
MS Clinical Psychology | APA Graduate Student Member
-
Emotional Dissonance vs Emotional Healing By Zohaib Ali (Zohaibmindscope | Mindscope Psychology)
ZohaibMindscope | Mindscope Psychology
Emotional Dissonance Insight
Insight by
Zohaib AliAre You Performing or Living?
One of the most misunderstood concepts in mental health is Emotional Dissonance. It arises when the emotions we express are fundamentally at odds with what we actually experience.
The Psychological Profile
Want to visually compare emotional dissonance vs healing?
👉 Explore the interactive comparison here.
“I feel anxious and irritable, but I keep smiling to meet expectations.”The Anatomy of Conflict
Why do we do it? And what does it cost us? Explore the triggers and the clinical implications of normalizing this state.
⚠Triggers of Dissonance
- •Social Expectations: The pressure to appear “put together” or happy in social settings.
- •Academic/Professional Pressure: Suppressing stress or confusion to perform competence.
- •Cultural Norms: Beliefs that expressing negative emotions is a sign of weakness or disrespect.
Clinical Implications (Click to Explore)
Select a symptom above to understand the psychological cost. -
Rumination Disorder Explained Simply in Urdu | Zohaib Ali (MindScope Psychology)
Author: Zohaib Ali
Qualification: MS Clinical Psychology Student
Platform: MindScope Psychology (Zohaibmindscope)
Zohaib Ali from MindScope Psychology – Learn mental health simply at Zohaibmindscope
-
Rumination Disorder Explained Simply | Zohaib Ali – MindScope Psychology
Rumination Disorder – Explained Simply by Zohaib Ali | MindScope Psychology
Rumination Disorder is a clinical feeding and eating disorder where a person
effortlessly regurgitates food after eating without nausea or vomiting.
This educational guide is created by Zohaib Ali,
an MS Clinical Psychology student, under the brand
MindScope Psychology, to help students and the public
learn mental health concepts simply at Zohaibmindscope.
What Happens in Rumination Disorder?
Unlike vomiting, rumination involves automatic regurgitation that feels
habitual rather than painful. After food returns to the mouth, individuals
may re-chew, re-swallow, or spit it out.Rumination Disorder vs Vomiting
Rumination Disorder is often misdiagnosed as reflux or vomiting.
Understanding these differences is critical for accurate diagnosis.Why Rumination Disorder Matters
- Dental erosion due to repeated acid exposure
- Weight loss and malnutrition
- Social embarrassment and avoidance
- Reduced quality of life
Treatment: Diaphragmatic Breathing
The most evidence-based treatment for Rumination Disorder is behavioral.
Diaphragmatic breathing after meals prevents the regurgitation reflex
by stabilizing abdominal pressure.
Author: Zohaib Ali
Qualification: MS Clinical Psychology Student
Platform: MindScope Psychology (Zohaibmindscope)
Zohaib Ali from MindScope Psychology – Learn mental health simply at Zohaibmindscope
-
What impact bad parenting has on child future?
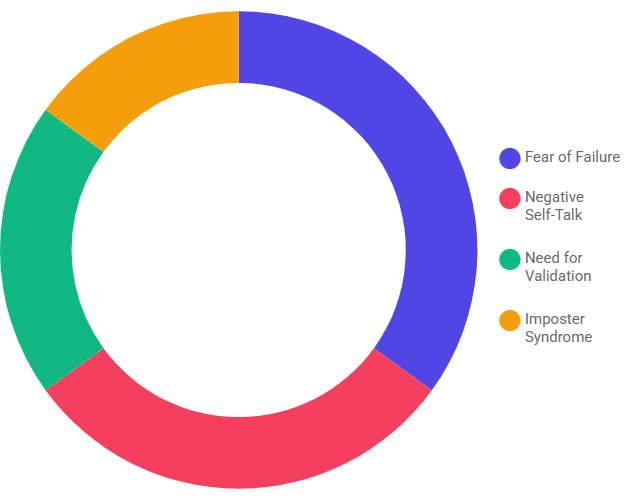
Bad parenting is not an isolated event; it is a catalyst for a developmental chain reaction. The struggles observed in adulthood—ranging from career stagnation to relationship instability—are often rooted in early childhood deficits. This analysis visualizes the mechanism by which low self-esteem, poor emotional regulation, and weak social skills compound over time to create long-term fragility.
The Cycle of Deficit
Developmental psychology identifies a specific pathway where early neglect transforms into adult dysfunction.
➔➔1. The Foundation: Self-Esteem
When parenting involves excessive criticism or lack of affirmation, children internalize a sense of worthlessness. They do not believe they are “enough.”
Key Insight
Low self-worth is the primary filter through which all future challenges are viewed, leading to risk aversion.
2. Emotional Regulation (ER)
Children learn to soothe themselves through co-regulation with parents. Without this, they lack the tools to manage stress.
- ✓Healthy: “I can handle this.”
- ✕Unhealthy: “I am overwhelmed/unsafe.”
Long-Term Impact Assessment
The deficits in self-esteem and regulation compound over decades, affecting specific domains of adult life.
🎓Education & Career
Fear of failure prevents the pursuit of ambitious goals. Difficulty with authority figures stems from early conflicts.
🤝Relationships
The “Attachment Template” is damaged. Adults may repeat unhealthy patterns or avoid intimacy entirely.
🧠Mental Well-being
Chronic stress and lack of coping mechanisms increase susceptibility to anxiety and depression.
-

Structuralism in Psychology
Structuralism in Psychology
An Early Scientific Approach to the Human Mind
🧪What Did Structuralists Do?
→They believed the mind could be studied like a science, applying systematic methods to mental processes.
→They used a method calledintrospection— asking trained subjects to describe, in detail, what they feel, see, or think immediately after a stimulus.
→Their goal was to find thebasic elements of thoughts— much like how chemists break matter into fundamental atoms.
🧠The Building Blocks of Consciousness
Structuralists focused on breaking down conscious experience into three primary, irreducible components:
👁️Sensations
The direct input from the physical world (what you feel, hear, smell, or see).
🖼️Images
The mental representations of objects not physically present (what you picture or remember).
🧓Key Pioneers
Wilhelm Wundt: He is widely considered the father of Structuralism and, more broadly, of experimental psychology. He established the first formal psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, in 1879.
Edward Titchener: Wundt’s student who brought a modified version of Structuralism to the United States, popularizing the school of thought in America.
📚Historical Importance
- Scientific Foundation: Structuralism played a crucial role in helping psychology break away from philosophy and establish itself as an independent, scientific discipline.
- Catalyst for Change: Its methods and theories served as the starting point and intellectual sparring partner for many other influential schools of thought in psychology that followed.
⚠️Key Criticisms
- Unreliable Method: Introspection was highly subjective and unreliable, as different individuals reported vastly different experiences for the same stimulus.
- Limited Scope: It struggled to study complex behaviors, animal psychology, emotions, or unconscious thoughts, which limited its explanatory power.
- Too Narrow: Later psychologists, particularly the Functionalists, argued that Structuralism was too focused on the *structure* of the mind and failed to explain the *purpose* or *function* of mental processes.

